Wear happens. Beamalloy’s patented Ion Beam Enhanced Deposition (IBED) surface treatments will help you improve your productivity by slowing it down. The result can be measured in real cost savings, increased production, and improved product quality.
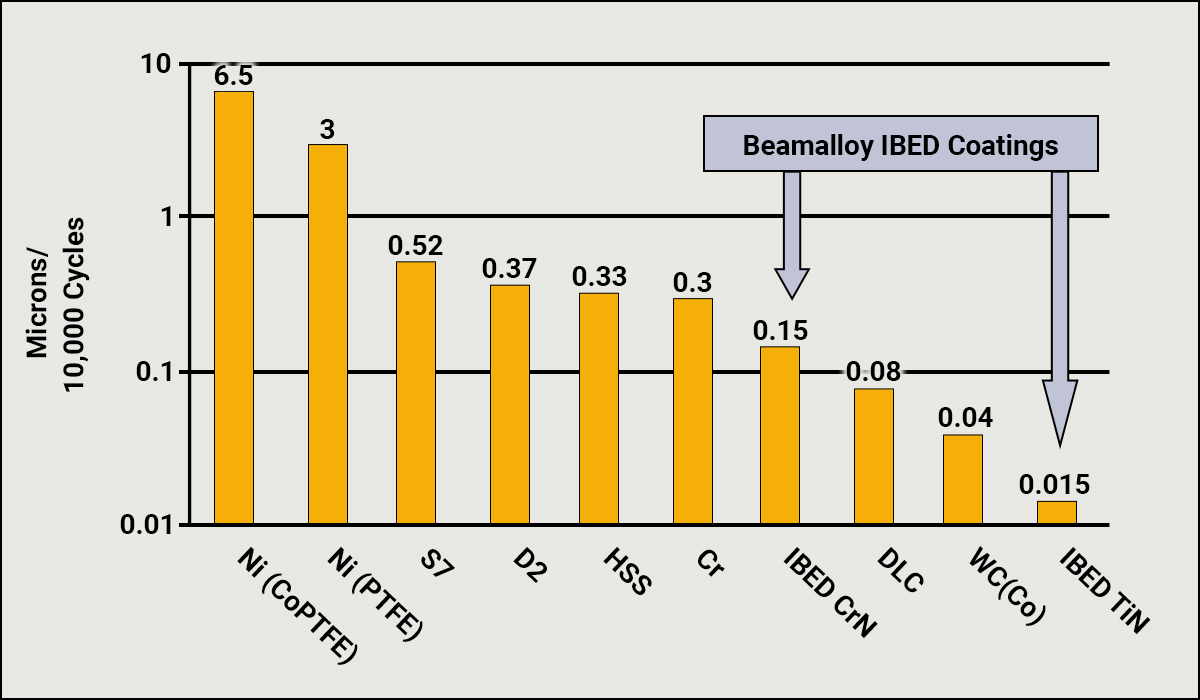
Material Matters. Taber Abraser wear testing clearly shows relative improvements in wear resistance of specific metal and ceramic surface treatments over standard and specialty metal tooling steels. Dramatic and destructive, this testing demonstrates the relative performance of various coatings.
Process Matters. Just like a bad paint job with the worlds best paint, performance results are highly dependent on application of any surface treatment. Whether it’s chrome or titanium nitride, Beamalloy’s IBED process delivers the best performance possible with the right material for your application.
A variety of coatings, designed to improve wear- and corrosion-resistance are available for use on a variety of substrates. To the extent that these coatings preserve the original finish of the working surfaces of the punches they can also act to help reduce sticking and improve release. Hard refractory nitride coatings such as Titanium Nitride and Chromium Nitride are deposited by using Beamalloy’s IBED process at temperatures low enough to eliminate the dimensional distortion or bulk softening of the punch. When formulations containing abrasive components, the use of Beamalloy IBED coatings can dramatically reduce tool wear and the need for continuous cleaning and re-polishing.
Taber Abraser Wear Rate
MIL-A-8625F
AMS

The performance of coated tools and components is determined by the wear properties of the coatings applied. The relative abrasive wear rate of materials and coatings can be measured by the Taber Abraser method by coating panels which are then run for a fixed number of cycles against abrasive-loaded resilient wheels. The actual wear rate in microns of thickness per cycle is measured providing a means for direct comparison of the wear performance of various materials and coatings. Soft coatings like electroless nickel are seen to wear much faster than hard materials such as tungsten carbide.
Ballistically Bonded Case Layer
Nano-crystalline Structure
Low Temperature Processing
Precise Surface Replication
Comparative Rates of Abrasive Wear
(microns per 10,000 cycles)